
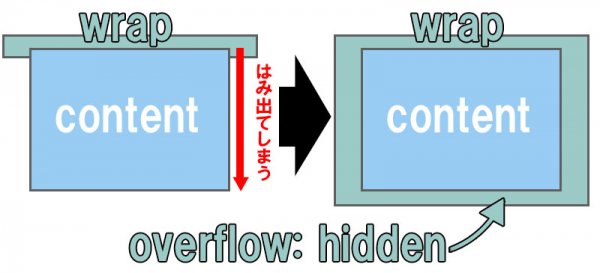


Well, if we simply move the position rule to put it just one level above, then the problem will be solved. It works the same if the parent is set to absolute instead of relative (an absolute inside another absolute) the first absolute acts as the positioning context for the second absolute.Īnyway, here our main problem is that the relative parent is also the overflow:hidden one.BTW, this is probably why they called it « re-la-tive », just sayin’ 😛.If no relative parent is found it will then reach the highest possible « container », which is the browser window, aka the viewport (or the document maybe, or the window … ? hey you know what, I’m not a W3C expert ok!).Knowing this, we can add a wrapper around the menus to act as the closest positioned ancestor for each submenu. In this case, the solution was as easy as targeting the body element as well as the child div content wrapper and applying css overflow: hidden styles to both. An absolutely positioned element is actually positioned regarding a relative parent, or the nearest found relative parent, which means it bubbles up the DOM until it finds a relative context to apply the positioning. Basically, in order for an absolutely positioned element to appear outside of an element with overflow: hidden, its closest positioned ancestor must also be an ancestor of the element with overflow: hidden.This can be used with overflow-clip-margin to set the clipped area. The CSS overflow property defines what to do when content overflows the content box, such as displaying the content outside of the content box, clipping the. clip: content is clipped when it proceeds outside its box. scroll: similar to hidden except users will be able to scroll through the hidden content. CSS do sucks a lot, even CSS3, I mean … ok no troll here 🙂īut first, if you’re trying to mess with these absolute/relative properties you really should be aware of these few important rules: hidden: overflowing content will be hidden. Well, usually it ends by putting the absolute element outside of the annoying overflow:hidden parent, and you grumbling about how CSS sucks and so on… Actually you’re quite right. Let’s say you need to absolute position something… And then you try to move it in some direction, and boom it disappears… You forgot the parent was set to overflow:hidden and now your element is lost in the hidden infinite vacuum. CSS overflow allows you to set up element behavior in. I believe, every front-end developer encountered this situation, at least once. When the content of an element is larger than the space provided by the element, the content may overflow. These values are used to either hide or clip overflowing content using specific approaches. With the hidden value, the overflow is clipped, and the rest of the content is hidden: You can use the overflow property when you want to have better control of.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
